Main Industries of Precision Molds and Mold Components
Precision mold components are the core elements of mold manufacturing. With their high dimensional accuracy and exceptional stability, they are widely used across industries that demand strict machining tolerances and product consistency. The main application sectors are as follows:

01
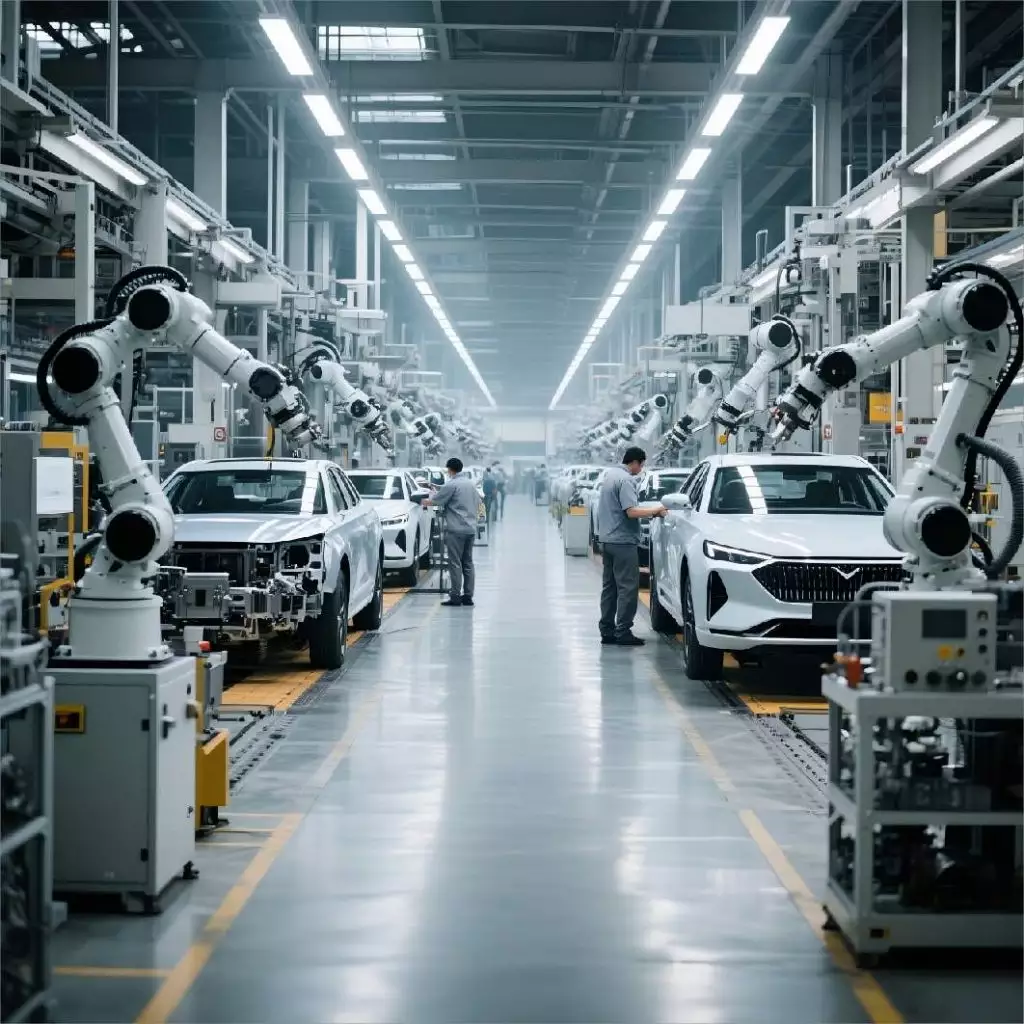
Automotive Manufacturing The automotive industry imposes stringent requirements on the accuracy, consistency, and durability of parts. Precision mold components are fundamental to producing key automotive components. Examples include mold core parts (such as dies, punches, guide posts, and bushings) used for manufacturing body panels (e.g., doors, hoods), interior components (e.g., dashboards, door trims), exterior fittings (e.g., bumpers, lamp housings), and powertrain elements (e.g., gears, bearing housings).
02
Electronics and 3C Industry (Computer, Communication, Consumer Electronics) 3C products are characterized by compact size and intricate structures, relying on precision molds for the mass production of miniature components. Examples include mold components such as micro punches, precision inserts, and vent blocks used in producing enclosures, camera modules, chip carriers, connectors, and PCB insert parts for mobile phones, laptops, and home appliances.

03
Medical Device Industry As medical equipment relates directly to human safety, mold components must meet exceptionally high standards in precision, cleanliness, and material stability. Typical applications include mold core components for forming disposable medical consumables such as syringes, blood collection tubes, IV sets, implantable devices, and surgical instruments.
04
Aerospace and Defense Industry This sector involves high-strength, high-temperature-resistant materials (e.g., titanium alloys, composite materials), requiring mold components capable of withstanding extreme processing conditions. Examples include mold assemblies such as precision mold frames and hot runner components used in the forging or casting of aircraft turbine blades, structural brackets, spacecraft components, and missile guidance parts.


05
Home Appliance and Consumer Goods Industry While precision requirements are relatively lower compared to the aforementioned sectors, precision mold components are still critical to ensuring product performance and appearance. Examples include injection mold components used in producing refrigerator liners, washing machine drums, and air conditioner housings, as well as forming molds for kitchenware (e.g., non-stick pans) and cosmetic packaging.
06
New Energy Industry In the production of lithium batteries and photovoltaic components, precision mold components are essential for manufacturing core parts. For example, punching dies for lithium battery electrode sheets (ensuring uniform thickness with tolerances ≤ 0.002 mm) and cutting mold assemblies for photovoltaic silicon wafers (ensuring high precision and minimal material waste).


07
Precision Instrument Industry Used in applications requiring extremely high standards of accuracy, surface finish, and tolerance control—such as optical lens housings, structural parts of measuring instruments, and sensor components. These applications often rely on ultra-precision mold processing.
08
Telecommunications Industry Applied in the production of structural and functional parts for communication equipment, such as routers, mobile communication modules, fiber optic connectors, and shielding covers. Molds used in this sector must support designs that demand miniaturization, high component density, electrical conductivity, and thermal performance.






